N Stage Lung Cancer
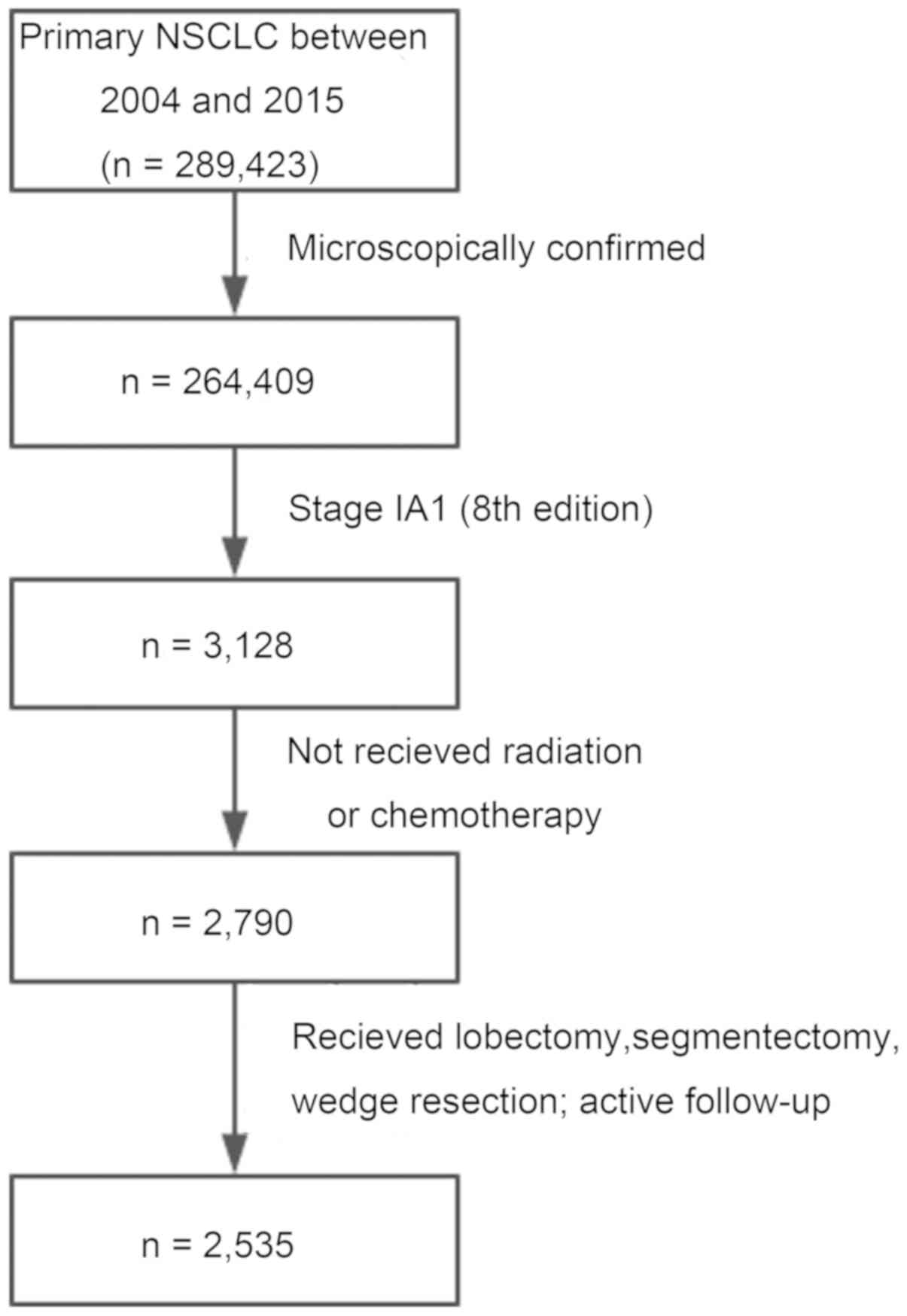
Conditional Survival Rate Estimates Of Lobectomy Segmentectomy And Wedge Resection For Stage Ia1 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer A Population Based Study

Pdf Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Evaluation Of 737 Consecutive Patients In A Single Institution

New Insights Into Stage And Prognosis In Small Cell Lung Cancer An Analysis Of 968 Cases Dayen Journal Of Thoracic Disease

Prognostic Factors In Resected Pathological N1 Stage Ii Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer European Respiratory Society

Tracking The Evolution Of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Nejm
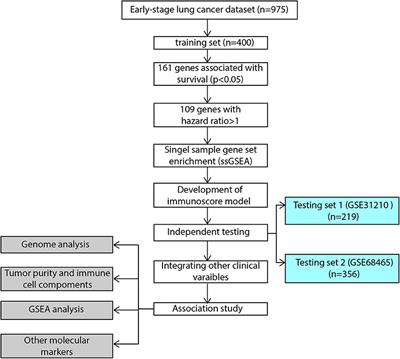
Frontiers Immunoscore Predicts Survival In Early Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients Oncology
A cancer is always referred to by the stage it was given at diagnosis, even if it gets worse or spreads New information about how a cancer has changed over time gets added on to the original stage So, the stage doesn't change, even though the cancer might How Stage Is Determined.

N stage lung cancer. Losing weight without trying;. Lung cancer with bone metastases refers to the spread of cancer from the primary (original) tumor to the bone The spread of cancer cells occurs either through the bloodstream or lymphatic system (a system of fluids, vessels, and organs that protect the body against foreign invaders). Lung cancer typically doesn't cause signs and symptoms in its earliest stages Signs and symptoms of lung cancer typically occur when the disease is advanced Signs and symptoms of lung cancer may include A new cough that doesn't go away;.
A diagnosis of stage 4 lung cancer indicates that the cancer has spread to the other lung or more distant parts of the body It is the final stage of lung cancer There is currently no cure, but. The TNM staging system is the most common way for doctors to stage non small cell lung cancer And it is sometimes used for small cell lung cancer TNM stands for Tumour, Node, Metastasis Doctors use the TNM system to create a number staging system, with stages 1 to 4. N0 is used to describe lung cancer that has no apparent lymph node involvement, Comparatively, N1 describes lung cancer that has also been identified in the ipsilateral intrapulmonary or hilar.
Stage 0 nonsmall cell lung cancer is an early stage of lung cancer that is only in the top lining of the lung can has not spread outside the lungs Stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is divided into two substages, 1A and 1B, based on the size of the tumor and whether it has spread to the lining of the lung. After someone is diagnosed with small cell lung cancer (SCLC), doctors will try to figure out if it has spread, and if so, how far This process is called staging The stage of a cancer describes how much cancer is in the body It helps determine how serious the cancer is and how best to treat it Doctors also use a cancer's stage when talking. Diagnoses of lepidic predominant adenocarcinoma, previously known as bronchoalveolar carcinoma (BAC) Unlike other forms of lung cancer that often spread to the lining of the lungs and other regions of the body, this type of cancer usually remains within one lung Earlystage lung cancer in which conventional treatments (eg, surgical lobectomy) are impossible due to poor lung function related to endstage COPD or other lung diseases These scenarios may be considered for lung.
Small Cell Lung Cancer Stages Limited stage It’s in just one lung and possibly nearby lymph nodes It hasn’t spread to both lungs or past your lungs Extensive stage Your tumor has spread to other areas of your lungs and chest It may have spread to the fluid around your lungs (called the pleura). Hi my father in law (dad) was diagnosed with stage 4 small cell lung cancer April 4 16 he was told 68 weeks to live without chemo n 912 with chemo it was such a shock he decided to do chemo, he got to round 2 n had to stop it would have killed him as he was so weak a couple of weeks later his gp came and said it wasn't months it was weeks (which means up to 4) he has looked at scans n the. Stage 0 nonsmall cell lung cancer is an early stage of lung cancer that is only in the top lining of the lung can has not spread outside the lungs Stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is divided into two substages, 1A and 1B, based on the size of the tumor and whether it has spread to the lining of the lung.
Stage 2a lung cancer indicates a tumor size of between 4 and 5 centimeters (roughly 1½ inch and 2 inches, respectively) The tumor will also have grown into an airway or tissues surrounding the lungs However, no lymph nodes will be affected, and there will be no evidence of metastasis;. Continued Outlook More people in the US die of lung cancer than of breast, colon, and prostate cancers combined About 1 in 3 people diagnosed with stage IIIA lung cancer live for at least 5. Lung cancer is the leading cause of death worldwide and 15 TS genes were significantly downexpressed in tumor samples of stage 1 We used Sscores and Nscores defined in correlation.
Subgroup analysis showed that for patients with 8th edition stage IB NSCLC, 5year OS was 876% in the observation group (n = 265) and 4% in the adjuvant group (p = 0021) For patients with 8th edition stage IIA NSCLC, 5year OS was 481% and 877% in the observation group and the adjuvant group (p < 0001), respectively. In cancer, there are 5 main stages 0, I, II, II and IV Thus, the fourth stage is the last Such cancer is sometimes called common, metastatic (as one of the most frequent and main characteristics of grade 4 lung cancer is the appearance of distant metastases in different organs) Tumor foci are found in both lungs. A cure is not possible.
Nonsmall cell lung cancer has four main stages Stage 1 Cancer is found in the lung, but it has not spread outside the lung Stage 2 Cancer is found in the lung and nearby lymph nodes. Stage 3 Cancer is in the lung and lymph nodes in the middle of the chest Stage 3A Cancer is found in lymph nodes, but only on the same side of the chest where cancer first started growing. Phase III study of (m)RNA expression did not confer significant advantage for stage IIIII lung cancer Download PDF Copy Reviewed by Emily Henderson, BSc Jan 31 21.
Understanding if and where lung cancer has spread (the stage) is important to determining what options are available for treatment. Lung cancer is the number one cause of cancer deaths in both men and women in the US and worldwide;. Lung cancer is the leading cause of death worldwide and 15 TS genes were significantly downexpressed in tumor samples of stage 1 We used Sscores and Nscores defined in correlation.
A diagnosis of stage 4 lung cancer indicates that the cancer has spread to the other lung or more distant parts of the body It is the final stage of lung cancer There is currently no cure, but. The displacement of functional tissue with malignant tissue will almost invariably reduce lung function—often minimally with earlystage cancer but more significantly as the disease progresses Reduced Lung Volume. In medicine, lung cancer staging is the assessment of the extent to which a lung cancer has spread from its original source As with most cancers, staging is an important determinant of treatment and prognosisIn general, more advanced stages of cancer are less amenable to treatment and have a worse prognosis The initial evaluation of nonsmall cell lung cancer staging uses the TNM.
In medicine, lung cancer staging is the assessment of the extent to which a lung cancer has spread from its original source As with most cancers, staging is an important determinant of treatment and prognosisIn general, more advanced stages of cancer are less amenable to treatment and have a worse prognosis The initial evaluation of nonsmall cell lung cancer staging uses the TNM. Extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ESCLC) is in the stage where it has spread to other parts of the body, such as the other lung or the brain Without treatment, the average life expectancy for a person with an extensivestage small cell lung cancer diagnosis is two to four months. In lung cancer, stages I, II, and III describe various sizes of primary tumour and lymph node involvement without distant metastasis Any distant metastasis is automatically stage IV Also used in combination with surgery for NSCLC and with chemotherapy for SCLC.
Stage 2b lung cancer indicates that the tumor is either less than 3 centimeters (1¼ inch) in diameter and. Lung cancer may not cause signs or symptoms in its early stages Some people with lung cancer have chest pain, frequent coughing, blood in the mucus, breathing problems, trouble swallowing or speaking, loss of appetite and weight loss, fatigue, or swelling in the face or neck. Most types of cancer have four stages stages I (1) to IV (4) Some cancers also have a stage 0 (zero) Stage 0 This stage describes cancer in situ, which means “in place”.
Symptoms of terminal cancer Profound fatigue is very common in the late stages of lung cancer Weight loss is also almost universal, and it occurs even when people are eating a diet with adequate calories Cancer cachexia, a syndrome including unintentional weight loss and muscle wasting, is very common in the later stages of cancer. The cost of lowdose CT is below $0, 2326 and surgery for stage I lung cancer is less than half the cost of latestage treatment 26,27 Using the original ELCAP data and the actual hospital. Lung carcinoid is a rare malignant tumor with poor survival The current study established a nomogram model for predicting cancerspecific survival (CSS) in patients with lung carcinoid tumors A total of 1956 patients diagnosed with primary lung carcinoid tumors were extracted from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database The specific predictors of CSS for lung carcinoid.
Passive exposure to tobacco smoke (passive smoking) also can cause lung cancer in nonsmokersThe two types of lung cancer, which grow and spread differently, are smallcell lung cancers (SCLC) and nonsmall. Chest Xrays are not effective in detecting early stage lung cancer However, lowdose CT scans have been shown to reduce lung cancer mortality by percent, according to a 11 study In the. Among the 412 participants with clinical stage I lung cancer — the only stage at which cure by surgery is highly likely — the estimated 10year survival rate was % (95% CI, 84 to 91), and.
At presentation, 30–40% of cases of NSCLC are stage IV, and 60% of SCLC are stage IV Survival for lung cancer falls as the stage at diagnosis becomes more advanced the English data suggest that around 70% of patients survive at least a year when diagnosed at the earliest stage, but this falls to just 14% for those diagnosed with the most advanced disease (stage IV). What Is Stage II (2) Lung Cancer?. Physical changes during the final stages of lung cancer can be related to the tumor in the lungs, the spread of cancer to other parts of the body, or due to the terminal stages of cancer in general By definition, the final stage of lung cancer implies that treatment options have been exhausted;.
Stage I means the cancer is small and only in one area This is also called earlystage cancer Stage II and III mean the cancer is larger and has grown into nearby tissues or lymph nodes Stage IV. In cancer, there are 5 main stages 0, I, II, II and IV Thus, the fourth stage is the last Such cancer is sometimes called common, metastatic (as one of the most frequent and main characteristics of grade 4 lung cancer is the appearance of distant metastases in different organs) Tumor foci are found in both lungs. It is the cancer most likely to lead to death, accounting for about % of the cancer mortality rate However, bronchogenic carcinoma is not homogeneous It is roughly split into two types depending on how the tumours look under a microscope smallcell lung cancers (SCLC) and nonsmall cell lung cancers (NSCLC).
Early signs may include 8 Persistent cough with dark or bloody phlegm Hoarse voice Chest pain Wheezing Frequent respiratory infections Fatigue or weakness Loss of appetite Unintended weight loss. For most cancers, stage 0 is called carcinoma in situ (CIS) "Stage 0 typically means that there are cancer cells that haven't penetrated through the lining or the initial wall," says David N. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in both men and women, according to the Lungevity FoundationThe disease claims the lives of approximately 156,000 Americans annually—and though you might feel like you're immune to this illness if you're a nonsmoker, the reality is that an estimated percent of people who die from lung cancer have never smoked or used tobacco products.
For most types of cancer, a biopsy is the only sure way for the doctor to know if an area of the body has cancer In a biopsy, the doctor takes a small sample of tissue for testing in a laboratory If a biopsy is not possible, the doctor may suggest other tests that will help make a diagnosis Lung cancer cannot be detected by routine blood work. Following a lung cancer diagnosis, doctors use staging systems to describe the size of tumors, whether or not they have spread, and to what extent With a defined stage, the disease can be properly treated according to its severityStage II (2) of lung cancer is still considered an early stage, yet some stage II cancers include metastases to nearby lymph nodes. Lung cancer is the leading cause of death worldwide and 15 TS genes were significantly downexpressed in tumor samples of stage 1 We used Sscores and Nscores defined in correlation.
Stages and grades of lung cancer The stage of a cancer tells you how big it is and whether it has spread Knowing the stage can help your doctor decide which treatment you need The tests and scans you have to diagnose your cancer give some information about the stage Sometimes it’s not possible to be certain about the stage of a cancer. It is the cancer most likely to lead to death, accounting for about % of the cancer mortality rate However, bronchogenic carcinoma is not homogeneous It is roughly split into two types depending on how the tumours look under a microscope smallcell lung cancers (SCLC) and nonsmall cell lung cancers (NSCLC). Background Enhancing tumorspecific Tcell immunity by inhibiting programmed death ligand 1 (PDL1)programmed death 1 (PD1) signaling has shown promise in the treatment of extensivestage smallcell lung cancer Combining checkpoint inhibition with cytotoxic chemotherapy may have a synergistic effect and improve efficacy Methods We conducted this doubleblind, placebocontrolled, phase 3.
Hi my father in law (dad) was diagnosed with stage 4 small cell lung cancer April 4 16 he was told 68 weeks to live without chemo n 912 with chemo it was such a shock he decided to do chemo, he got to round 2 n had to stop it would have killed him as he was so weak a couple of weeks later his gp came and said it wasn't months it was weeks (which means up to 4) he has looked at scans n the. For example, if you're diagnosed with stage II lung cancer, that's what it will be called, whether it spreads or goes into remission That's when cancer cells are gone. Cancers categorized as nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) make up approximately 85 percent of cancers beginning in the lungs Like stage I (1) NSCLC, stage II diagnoses are still earlystage cancers and may be cured by treatment or a combination of treatments.
The stages of nonsmallcell lung cancer are outlined below Stage 1 The cancer is contained within the lung and hasn't spread to nearby lymph nodes Stage 1 can also be divided into two substages stage 1A – the tumour is less than 3cm in size (12 inches) stage 1B – the tumour is 35cm (122 inches) Stage 2 Stage 2 is divided into two substages 2A and 2B In stage 2A lung cancer, either. Stage 4b lung cancer, in which cancer has spread to multiple places in one or more distant organs, such as the brain, adrenal gland, bone, liver, or distant lymph nodes Stage 4 lung cancer is incurable Treatments, therefore, are focused on slowing the progression of the disease, minimizing symptoms, and maintaining an optimal quality of life. In cancer, there are 5 main stages 0, I, II, II and IV Thus, the fourth stage is the last Such cancer is sometimes called common, metastatic (as one of the most frequent and main characteristics of grade 4 lung cancer is the appearance of distant metastases in different organs) Tumor foci are found in both lungs.
Coughing up blood, even a small amount;. Chest Xrays are not effective in detecting early stage lung cancer However, lowdose CT scans have been shown to reduce lung cancer mortality by percent, according to a 11 study In the. People in this stage of dying may have periods of no breathing, or they may breathe quickly followed by periods of slow breathing If they have developed pneumonia from being unable to clear the secretions from the airway, they may develop a fever This could actually hasten their death and is not uncommon in patients with lung cancer.
In lung cancer patients, acute pain is often felt in the chest and lumbar (lower back) regions of the body Approximately percent of patients with lung cancer present with chest pain at diagnosis, and pain increases in severity as lung cancer advances, with patients at later stages of the disease experiencing more pain 1. Doctors also use a cancer's stage when talking about survival statistics The earliest stage of NSCLC is stage 0 (also called carcinoma in situ, or CIS) Other stages range from I (1) through IV (4) As a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread A higher number, such as stage IV, means cancer has spread more. Cigarette smoking is the principal risk factor for the development of lung cancer;.
Extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ESCLC) is in the stage where it has spread to other parts of the body, such as the other lung or the brain Without treatment, the average life expectancy for a person with an extensivestage small cell lung cancer diagnosis is two to four months.

Risk Factors For Recurrence And Unfavorable Prognosis In Patients With Stage I Non Small Cell Lung Cancer And A Tumor Diameter Of Mm Or Less Journal Of Thoracic Oncology
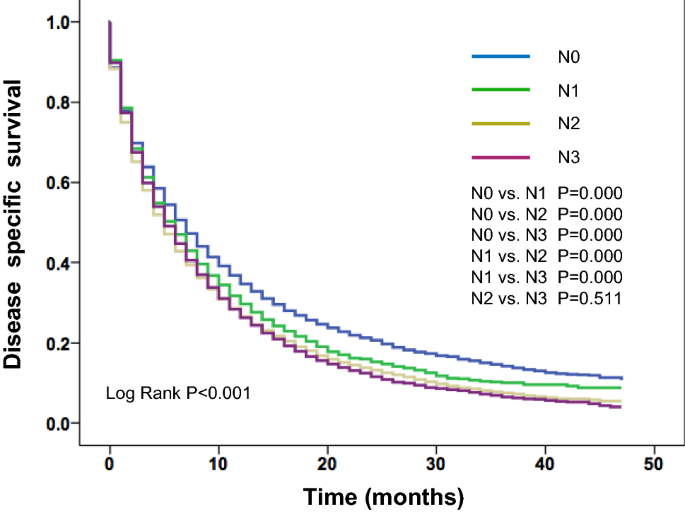
The Prognostic Impact Of Lymph Node Metastasis In Patients With Non Small Cell Lung Cancer And Distant Organ Metastasis Springerlink

Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Staging Imaging And Treatment Considerations Radiographics

The Diagnosis Tnm Staging And Management Of Lung Cancer In All Cases N Download Table

The Radiology Assistant Lung Cancer Tnm 8th Edition
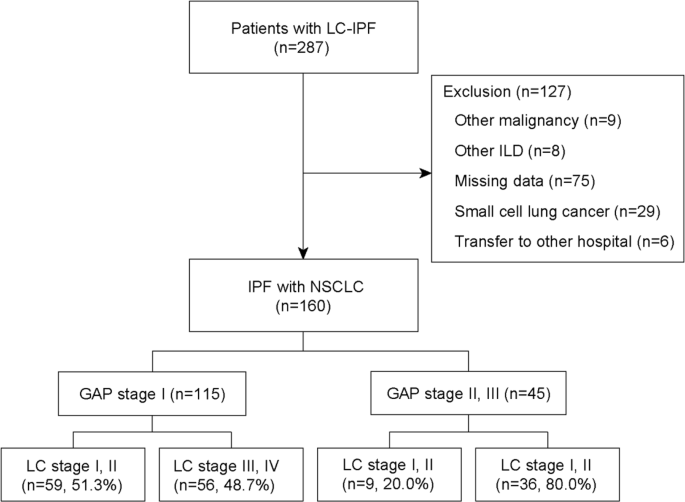
Prognosis Of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer In Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Scientific Reports

Chest Medicine Made Easy Dr Deepu 8th Edition New Tnm Staging Of Lung Cancer Changes From 7th Edition
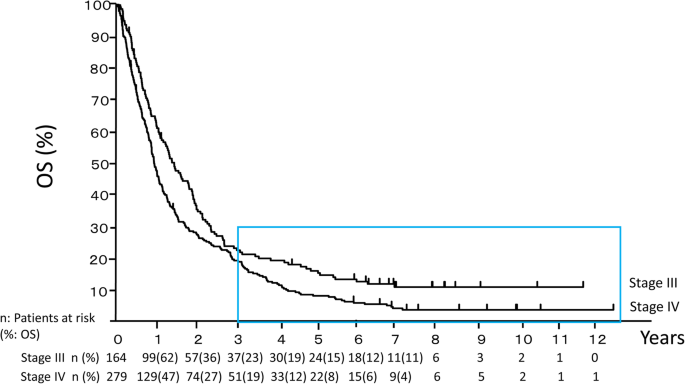
Analysis Of Key Clinical Features For Achieving Complete Remission In Stage Iii And Iv Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Respiratory Research Full Text

Pathology Outlines Staging

Exosomal Lipids For Classifying Early And Late Stage Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Anal Chim Acta X Mol

Disparities In Guideline Concordant Treatment For Pathologic N1 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Sciencedirect
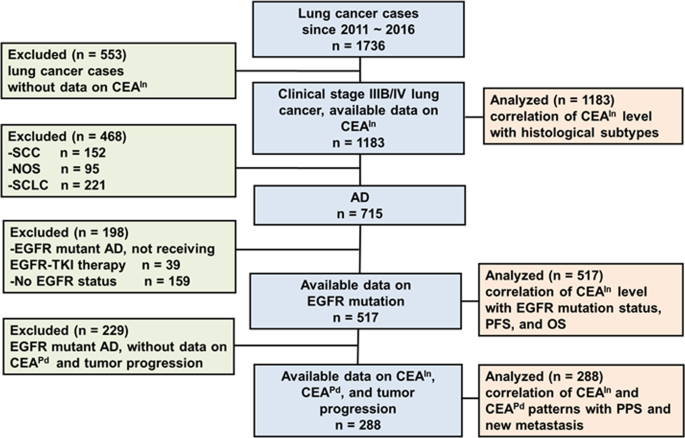
Association Of Divergent Carcinoembryonic Antigen Patterns And Lung Cancer Progression Scientific Reports

Analysis Of Advanced Lung Cancer Patients Diagnosed Following Emergency Admission European Respiratory Society

Methods For Staging Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Chest
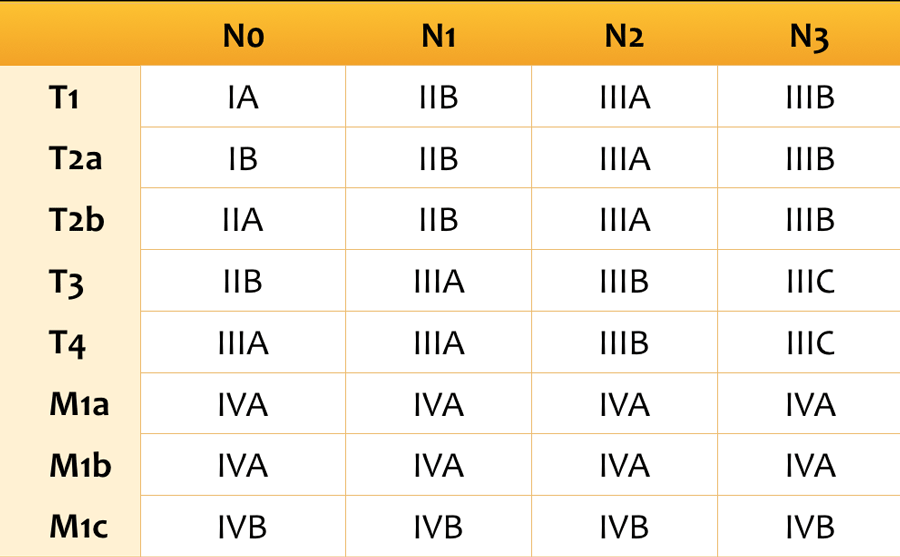
The Radiology Assistant Tnm Classification 8th Edition
Http Cancerstaging Org References Tools Quickreferences Documents Lungmedium Pdf

Nodal Recurrence After Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy For Early Stage Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Incidence And Proposed Risk Factors Cancer Treatment Reviews

Lung Cancer Staging Download Table
Q Tbn And9gctlkzr87kr1jpirbexncdlbkp5j5uvtqwkl4hv7zrgevdy5oazt Usqp Cau

The International Association For The Study Of Lung Cancer Lung Cancer Staging Project Proposals For The Revision Of The Clinical And Pathologic Staging Of Small Cell Lung Cancer In The Forthcoming Eighth
Overall Survival Os According To Lung Cancer Stage N 595 Download Scientific Diagram

Staging Lung Cancer

Survival Of Patients With Stage I Lung Cancer Detected On Ct Screening Nejm

Adjuvant Chemotherapy May Improve Prognosis After Resection Of Stage I Lung Cancer With Lymphovascular Invasion The Journal Of Thoracic And Cardiovascular Surgery

Learnoncology

Lung Cancer Staging And Tnm Classification Ppt Download

Preoperative Staging Of Lung Cancer With Combined Pet Ct Nejm
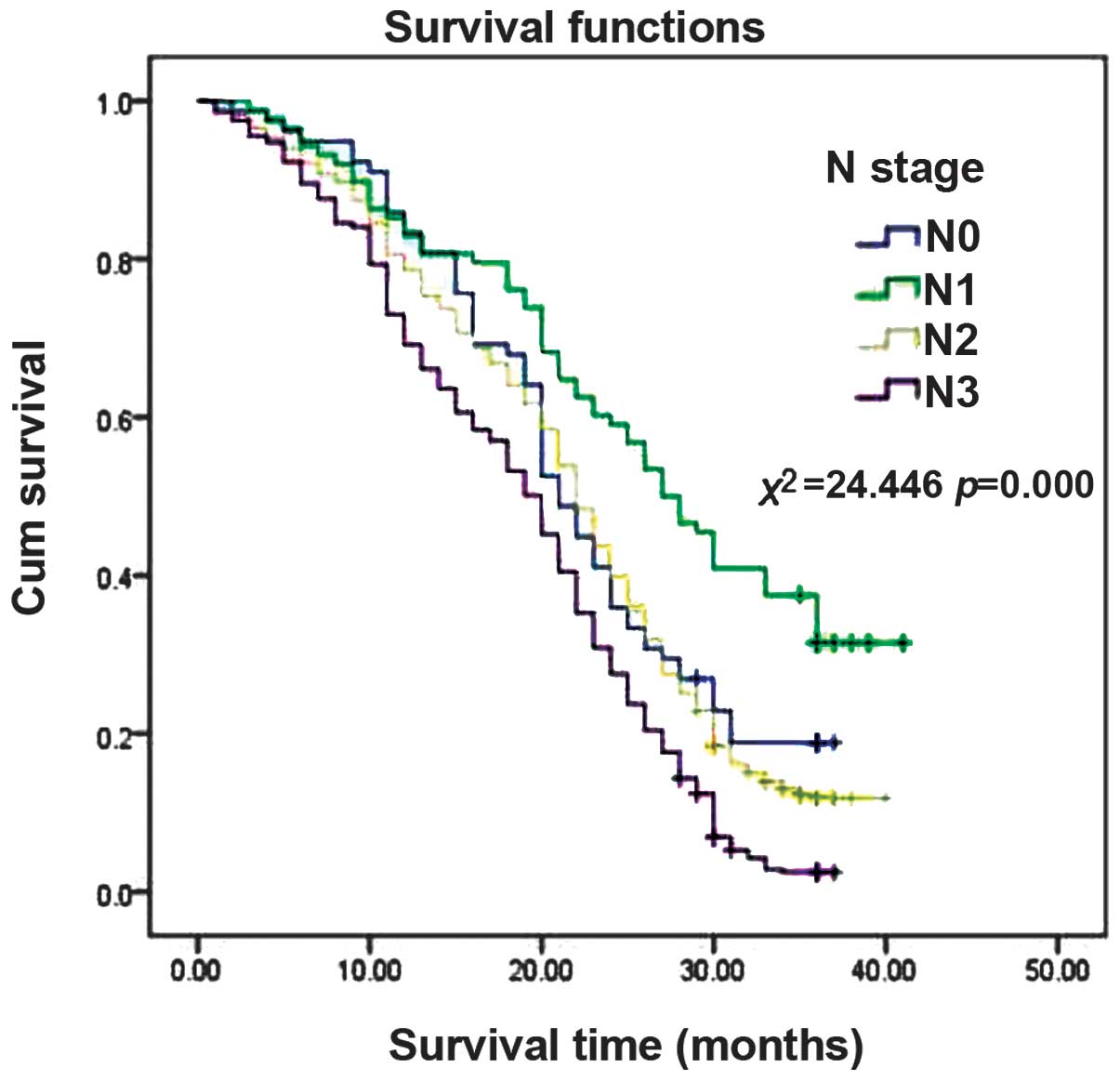
Clinical Investigation Into The Initial Diagnosis And Treatment Of 1 168 Lung Cancer Patients
Lung Cancer Staging The Noninvasive Tools

Ultra Late Recurrence Of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Over 10 Years After Curative Resection Oncology Nurse Advisor

The Optimal Treatment For Stage Iiia N2 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer A Network Meta Analysis The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery

Stage Distribution Of Lung Cancer In Pancan Nlst And Ontario Studies Download Scientific Diagram

The Quality Of Peer Reviewed Publications On Surgery For Early Stage Lung Cancer Within The Veterans Health Administration Seminars In Thoracic And Cardiovascular Surgery

A Prognostic Model For Overall Survival Of Patients With Early Stage Non Small Cell Lung Cancer A Multicentre Retrospective Study The Lancet Digital Health
Q Tbn And9gcqcxfecnmycv5ln8pzfopdakanue7mogtxftkth Gcc26iexbae Usqp Cau

The Eighth Edition Lung Cancer Stage Classification Sciencedirect

Preoperative Staging Of Lung Cancer With Combined Pet Ct Nejm
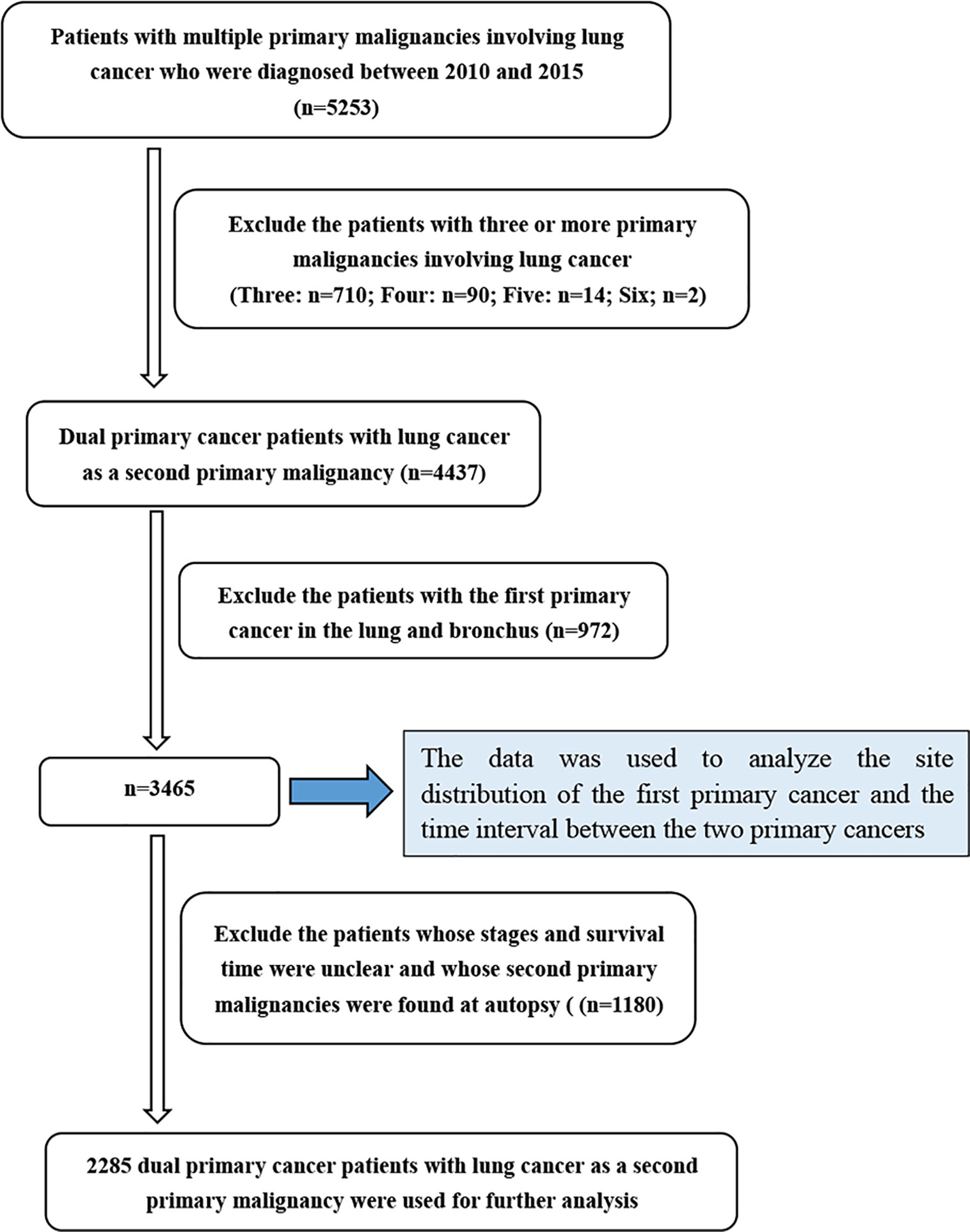
Frontiers Dual Primary Cancer Patients With Lung Cancer As A Second Primary Malignancy A Population Based Study Oncology

Phase I Trial Of Pembrolizumab And Radiation Therapy After Induction Chemotherapy For Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Journal Of Thoracic Oncology

Staging Of Lung Cancer Semantic Scholar
.jpg.aspx?width=800&height=125)
Lung Cancer Canada Lung Cancer Canada

Prognostic Study For Survival Outcome Following The Treatment Of Second Primary Lung Cancer In Patients With Previously Resected Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Wu Thoracic Cancer Wiley Online Library

Regional Emphysema Score Predicting Overall Survival Quality Of Life And Pulmonary Function Recovery In Early Stage Lung Cancer Patients Journal Of Thoracic Oncology

Ajcc Quick References
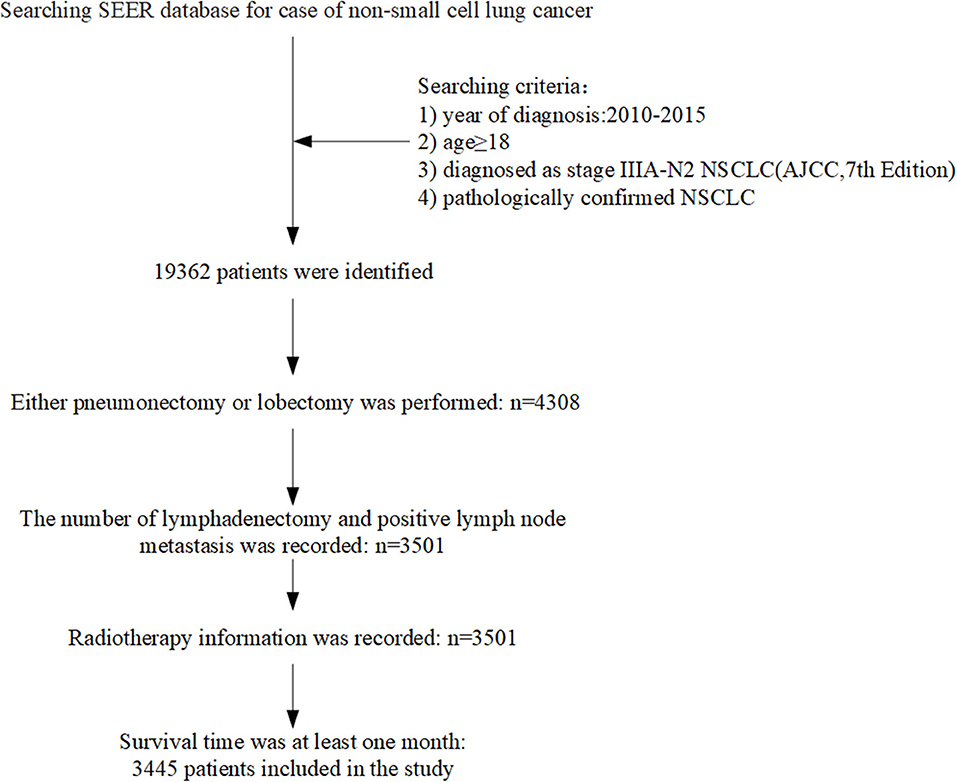
Frontiers Evaluation Of Postoperative Radiotherapy Effect On Survival Of Resected Stage Iii N2 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Oncology

The Stage Classification Of Lung Cancer Chest

Treatment And Outcome Of 432 Patients With Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer In First Second And Third Line Results From The Prospective German Tlk Cohort Study Lung Cancer
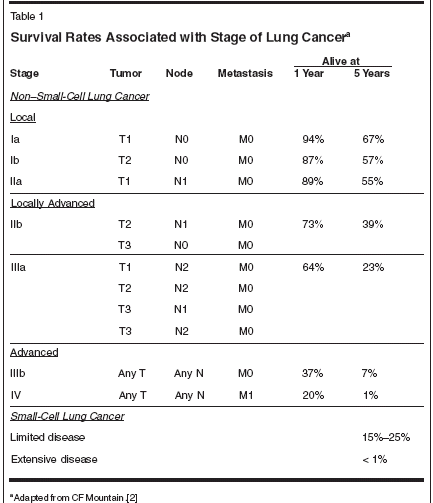
Overview And State Of The Art In The Management Of Lung Cancer Cancer Network

Prognostic Impact Of Preoperative Comorbidities In Geriatric Patients With Early Stage Lung Cancer Significance Of Sublobar Resection As A Compromise Procedure Lung Cancer

Time To Treatment And Survival In Veterans With Lung Cancer Eligible For Curative Intent Therapy Respiratory Medicine

The Radiology Assistant Lung Cancer Tnm 8th Edition

Analysis Of First Recurrence And Survival In Patients With Stage I Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated With Surgical Resection Or Stereotactic Radiation Therapy The Journal Of Thoracic And Cardiovascular Surgery

A Randomized Trial Comparing Preoperative Chemotherapy Plus Surgery With Surgery Alone In Patients With Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Nejm

Ablation Therapy For Advanced Stage Non Small Cell Lung Cancer A National Cancer Database Study Journal Of Vascular And Interventional Radiology

Talking About Lung Cancer Staging With Dr Mitchell Magee Thoracic Surgery

The Radiology Assistant Tnm Classification 8th Edition

Lung Cancer Staging Of The Patient Cohort By Dataset Download Table

Chest Radiology

Increasing Rates Of No Treatment In Advanced Stage Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients A Propensity Matched Analysis Journal Of Thoracic Oncology

Egfr Mutations In Early Stage And Advanced Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma Analysis Based On Large Scale Data From China Pi 18 Thoracic Cancer Wiley Online Library

Ten Year Patient Journey Of Stage Iii Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients A Single Center Observational Retrospective Study In Korea Realtime Automatically Updated Data Warehouse In Health Care Universe Root Study Lung Cancer
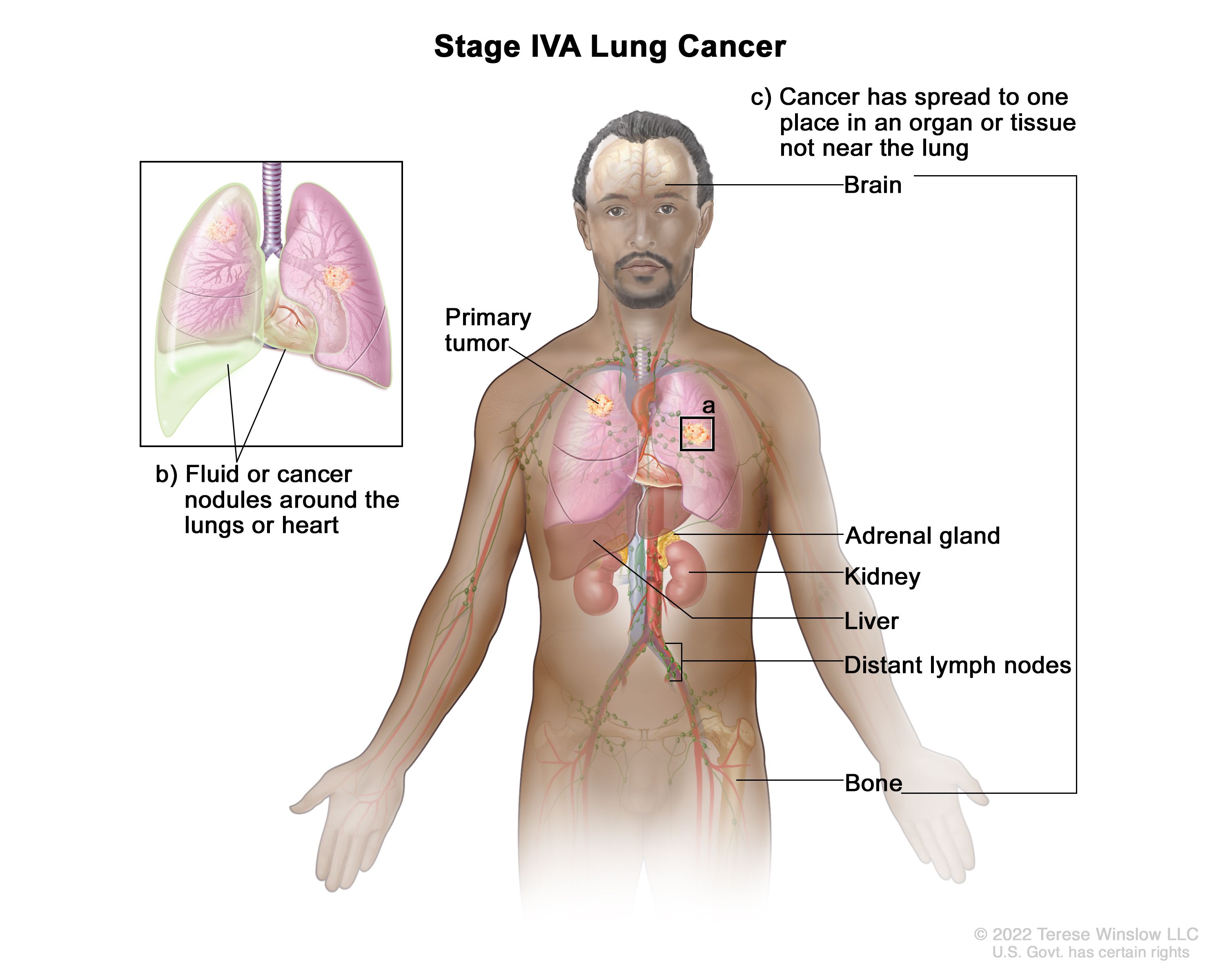
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Pdq Health Professional Version National Cancer Institute

Stage Lung Cancer

Full Text 1 3 And 5 Year Survival Among Early Stage Lung Cancer Patients Tre Lctt

Diagnostic Surgical Pathology In Lung Cancer Chest

Survival Of Patients With Stage I Lung Cancer Detected On Ct Screening Nejm
Www mr Org Ar Secciones Oncologia Chest 17 151 1 193 Pdf

Comparison Of Prognostic Impact Of Lymphovascular Invasion In Stage Ia Non Small Cell Lung Cancer After Lobectomy Versus Sublobar Resection A Propensity Score Matched Analysis Lung Cancer

Patterns Of Disease Recurrence After Sabr For Early Stage Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Optimizing Follow Up Schedules For Salvage Therapy Journal Of Thoracic Oncology

Survival Curve Indicating The Effect Of The Lung Cancer N Stage On Download Scientific Diagram
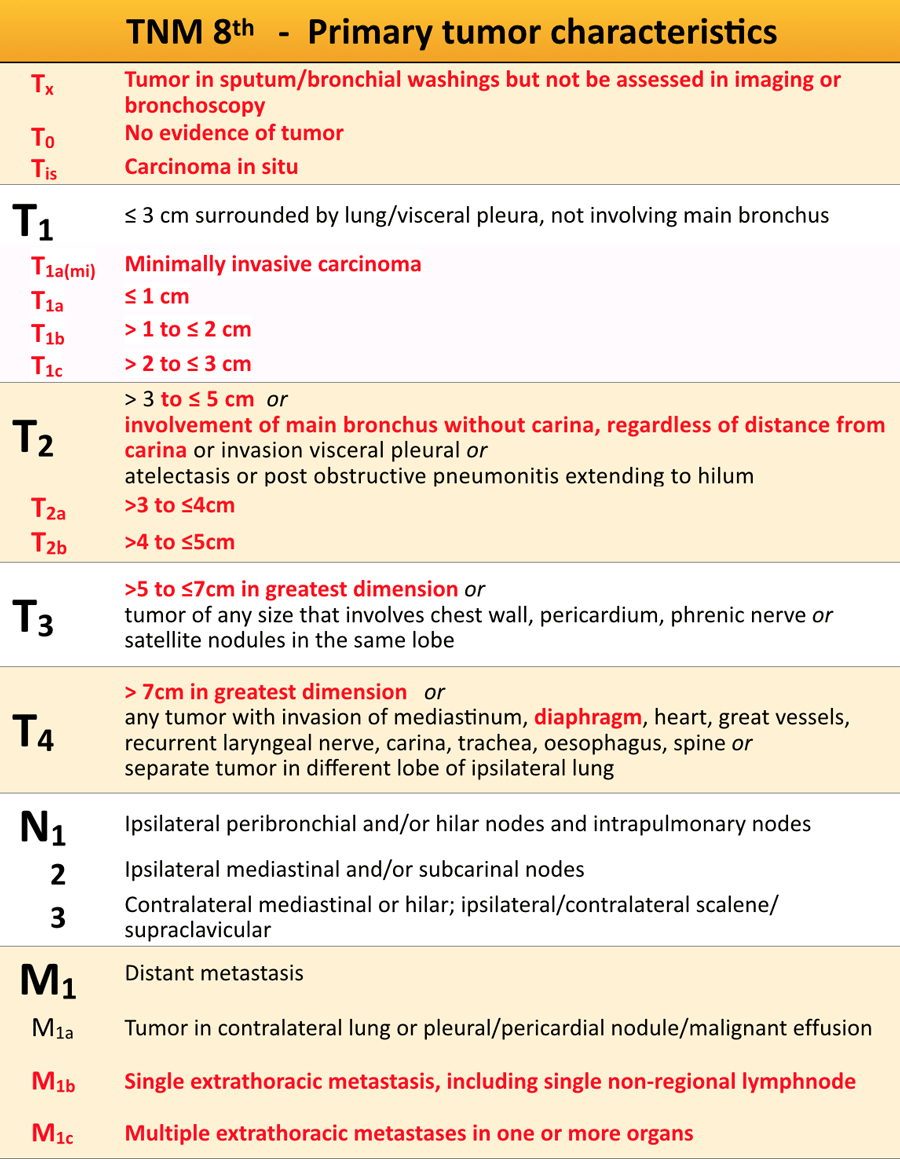
The Radiology Assistant Tnm Classification 8th Edition

Incidence Of Second Malignancy After Successful Treatment Of Limited Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer And Its Effects On Survival Journal Of Thoracic Oncology

County Level Variations In Receipt Of Surgery For Early Stage Non Small Cell Lung Cancer In The United States Chest

Undetectable Circulating Tumor Dna Levels Correlate With Low Risk Of Recurrence Metastasis In Postoperative Pathologic Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients Lung Cancer
Q Tbn And9gcsxrw Nieha 2ddeghjy5itsuwlz 4cdqfcp Rgu Krmcuezhc Usqp Cau

Lymphovascular Invasion As A Prognostic Indicator In Stage I Non Small Cell Lung Cancer A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery

Pathological Upstaging And Treatment Strategy Of Clinical Stage I Small Cell Lung Cancer Following Surgery Saji Journal Of Thoracic Disease

In Search Of The Philosopher S Stone The Alchemist Study For Lung Cancer The Bulletin

Evidence For Surgical Resections In Oligometastatic Lung Cancer Fernandez Journal Of Thoracic Disease

The 8 Th Lung Cancer Tnm Classification And Clinical Staging System Review Of The Changes And Clinical Implications Lim Quantitative Imaging In Medicine And Surgery

Impact Of Surveillance After Lobectomy For Lung Cancer On Disease Detection And Survival Clinical Lung Cancer

Factors Associated With Treatment Of Clinical Stage I Non Small Cell Lung Cancer A Population Based Analysis Clinical Lung Cancer

Circulating Levels Of Immune And Inflammatory Markers And Long Versus Short Survival In Early Stage Lung Cancer Annals Of Oncology
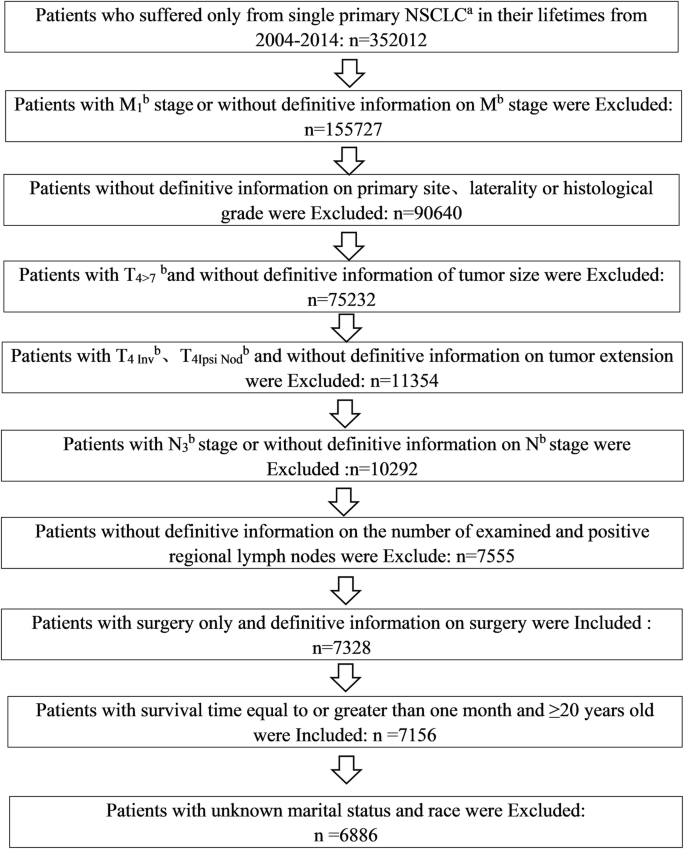
Rnsclc Prsp Software To Predict The Prognostic Risk And Survival In Patients With Resected T 1 3 N 0 2 M 0 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Biodata Mining Full Text
Q Tbn And9gcrro5gzxkzfnizjolvaoizrdbacpdprocrinhqwjy2wm0su6lk3 Usqp Cau

Effect Of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation On Early Stage Non Small Cell Lung Cancer According To The 8th Tnm Classification Lung Cancer
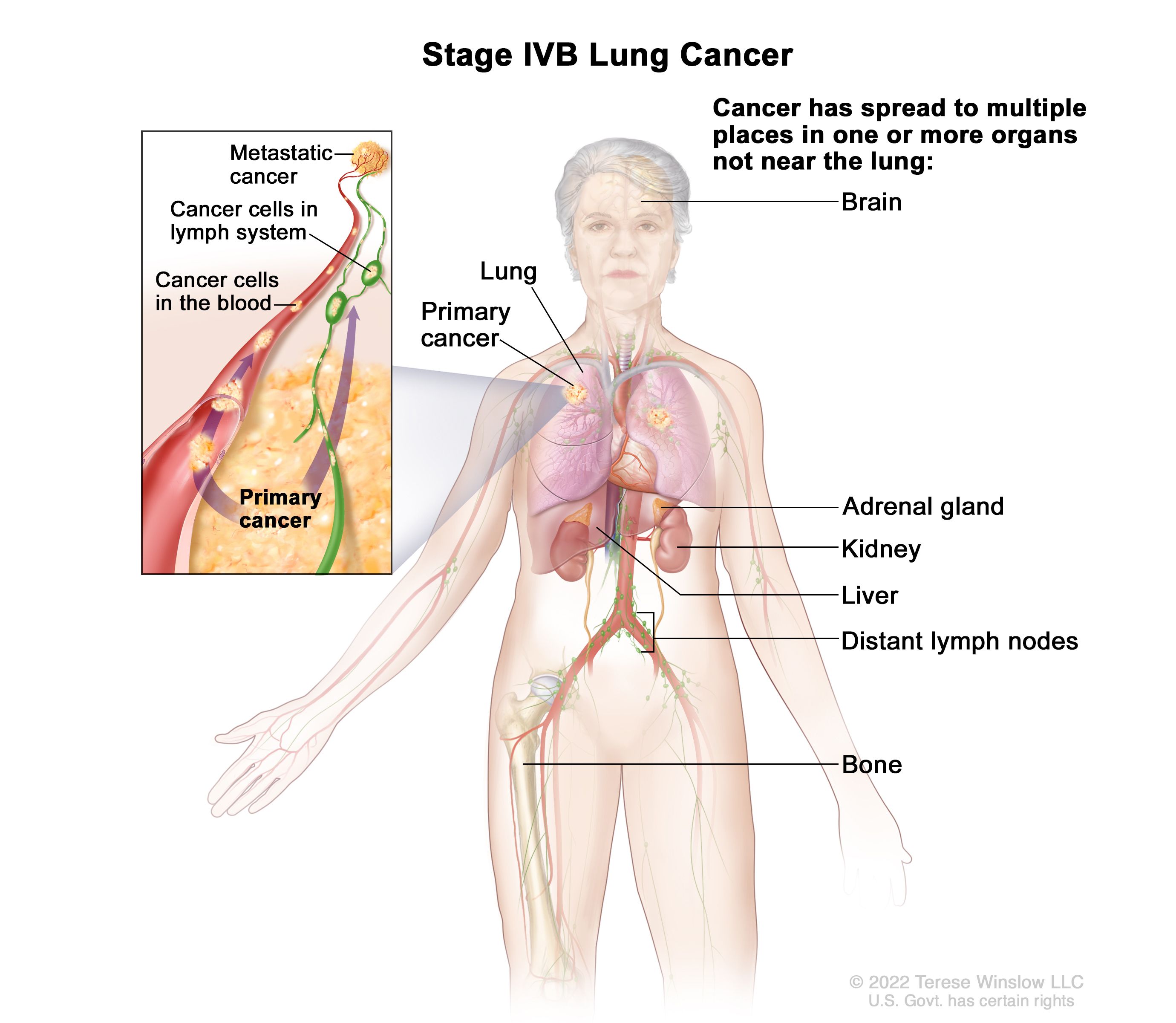
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Pdq Health Professional Version National Cancer Institute
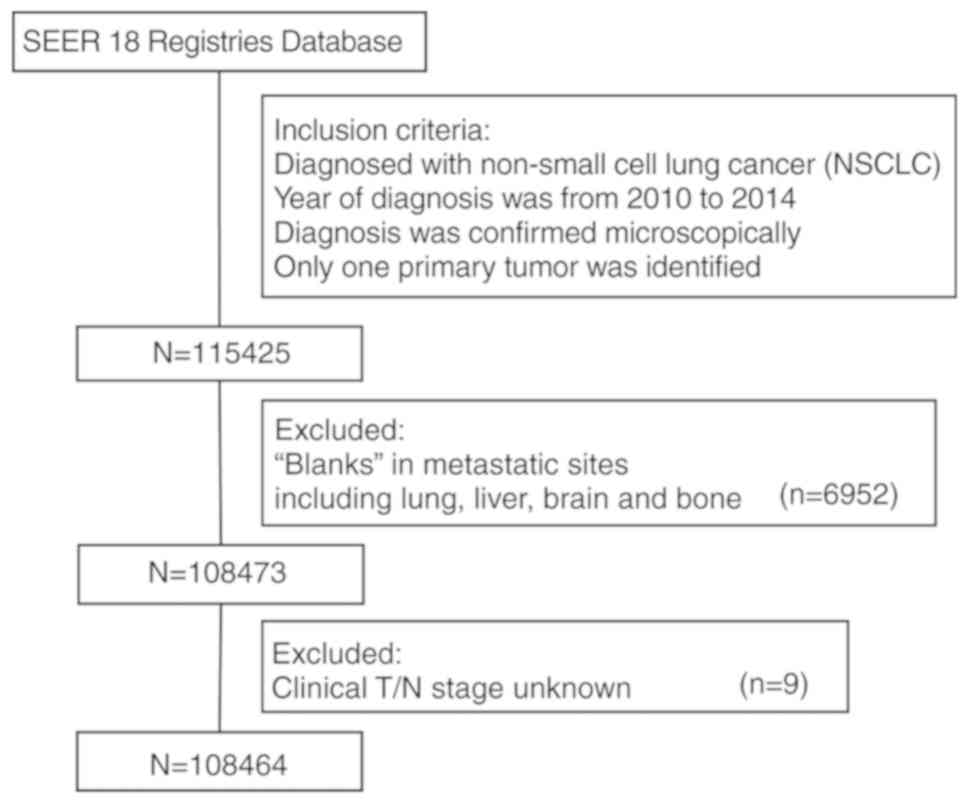
Clinical Associations And Prognostic Value Of Site Specific Metastases In Non Small Cell Lung Cancer A Population Based Study
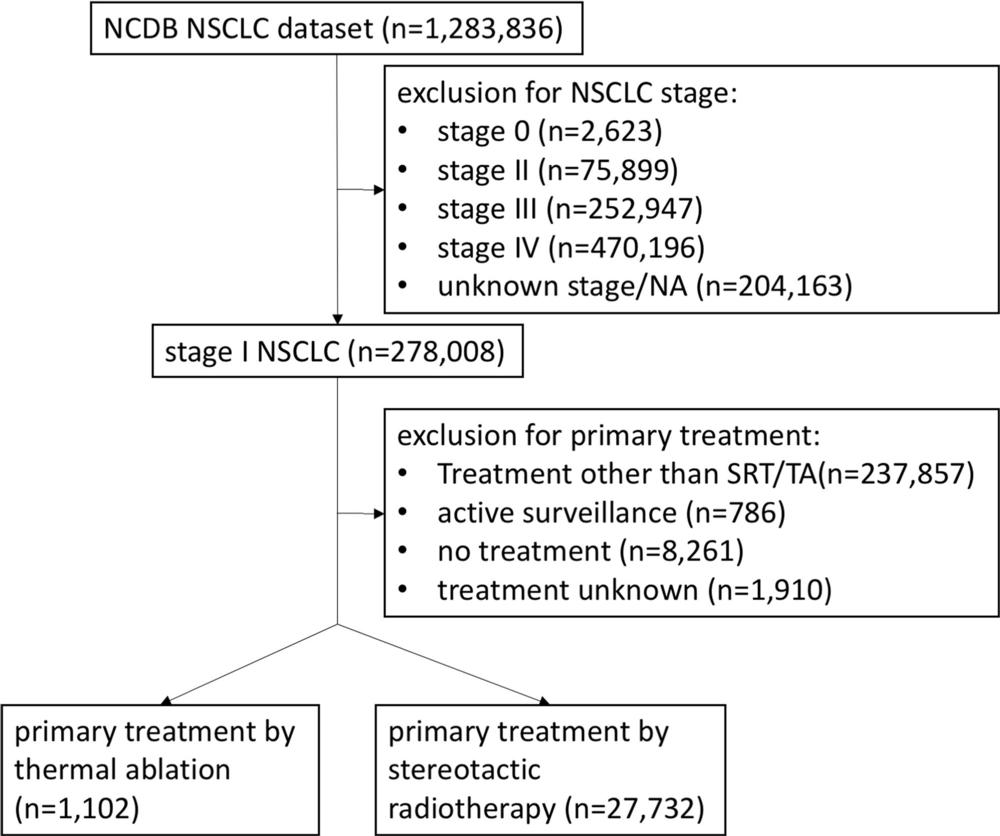
Thermal Ablation Effectively Treats Early Stage Lung Cancer

Clinical Staging Of Stage I Non Small Cell Lung Cancer In The Netherlands Need For Improvement In An Era With Expanding Nonsurgical Treatment Options Data From The Dutch Lung Surgery Audit The Annals

Prognosis After Wedge Resection In Patients With 8 Th Edition Tnm Stage Ia1 And Ia2 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Moon Journal Of Thoracic Disease

Role Of Fdg Pet Ct In The Eighth Edition Of Tnm Staging Of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Radiographics

Trend Analysis For Lung Cancer Stage Of Presentation By Insurance Type Download Table
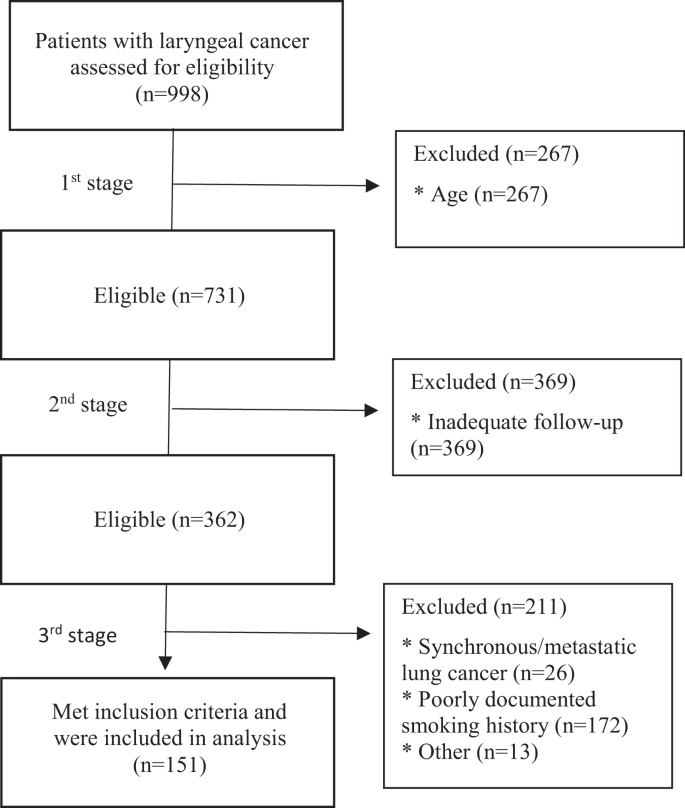
Ct Lung Screening In Patients With Laryngeal Cancer Scientific Reports

Tnm Staging Of Lung Cancer A Quick Reference Chart Sciencedirect
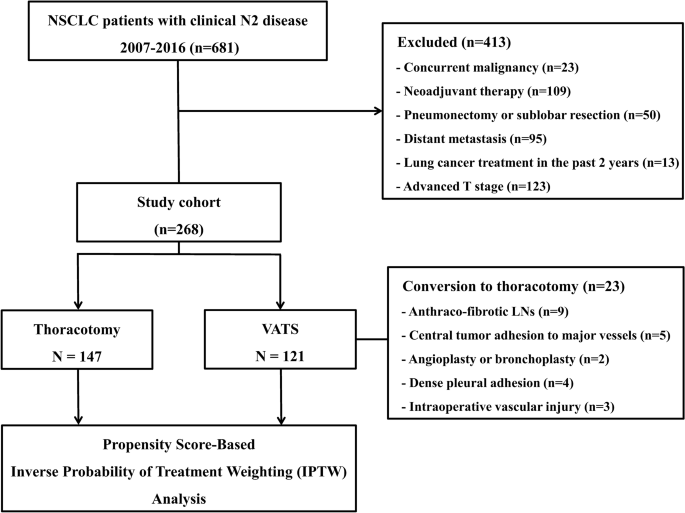
Video Assisted Thoracoscopic Lobectomy Is Feasible For Selected Patients With Clinical N2 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Scientific Reports

Effect Of Histological Subtype And Treatment Modalities On T1 2 N0 1 Small Cell Lung Cancer A Population Based Study Moon 19 Thoracic Cancer Wiley Online Library

The Iaslc Lung Cancer Staging Project Proposals For Revision Of The Tnm Stage Groupings In The Forthcoming Eighth Edition Of The Tnm Classification For Lung Cancer Journal Of Thoracic Oncology



